QCM-D
Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation Monitoring
Manufacturer:
external page Q-Sense AB, Sweden
Model:
E4
General Description:
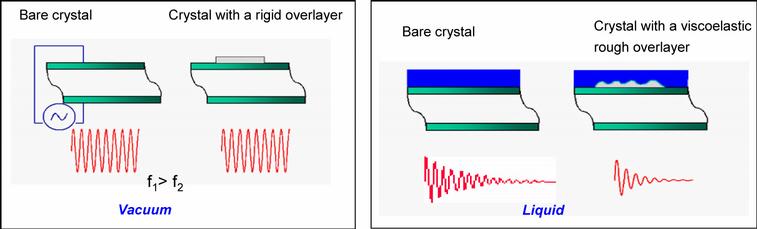
The Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation Monitoring (QCM-D) is a high-resolution mass sensing technique. It is used to observe and quantify molecular adsorption processes on a solid-liquid interface. Molecules or particles adsorbing on the sensor surface are causing a resonance frequency shift of the quartz crystal sensor, which is measured based on the piezoelectric effect. Apart form the adsorbed mass, the QCM-D can also gain infromation about the rigidity of an adsorbed layer via dissipation monitoring.
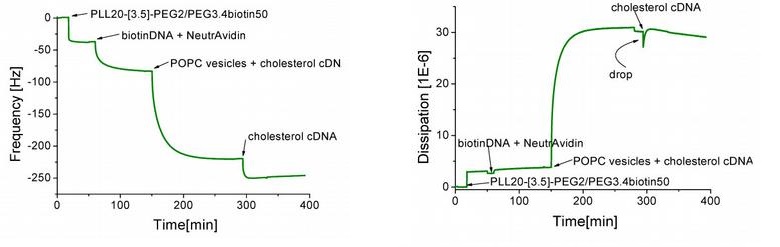
Typical measurements performed on a QCM-D are protein adsorption/interactions to/on a solid-liquid interface, lipid bilayer formation, lyposome or nanoparticle adsorption and polyelectrolyte multilayer formation.
Technical information:
The QCM-D reaches a detection limit in the order of 1 ng/cm2 on a sensor surface of 2 cm2 and a chamber volume of 300 ul. QCM-D sensor crystals are commercially available with a large variaty of surface coatings and modifications.
The E4 has four flow cells, wich can be operated in parallel and additionally has the ability to combine a QCM-D measurement with electrochemical procedures on the same electrode surface.